- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录3872 > PIC18F4450T-I/ML (Microchip Technology)IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX16 44QFN
204
XMEGA A [MANUAL]
8077I–AVR–11/2012
The TWI bus is a simple and efficient method of interconnecting multiple devices on a serial bus. A device connected to
the bus can be a master or slave, where the master controls the bus and all communication.
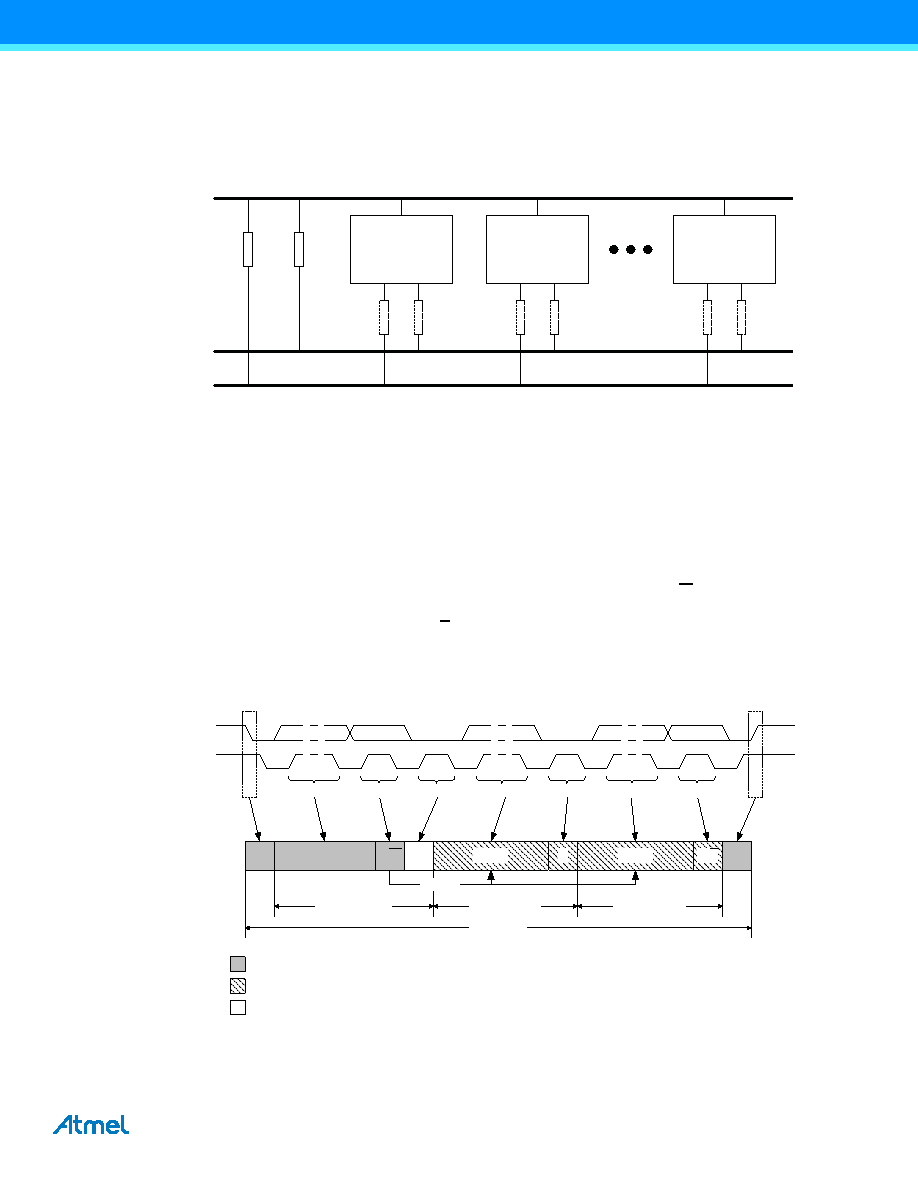
Figure 19-1 on page 204 illustrates the TWI bus topology.
Figure 19-1. TWI bus topology.
A unique address is assigned to all slave devices connected to the bus, and the master will use this to address a slave
and initiate a data transaction.
Several masters can be connected to the same bus, called a multi-master environment. An arbitration mechanism is
provided for resolving bus ownership among masters, since only one master device may own the bus at any given time.
A device can contain both master and slave logic, and can emulate multiple slave devices by responding to more than
one address.
A master indicates the start of a transaction by issuing a START condition (S) on the bus. An address packet with a slave
address (ADDRESS) and an indication whether the master wishes to read or write data (R/W) are then sent. After all
data packets (DATA) are transferred, the master issues a STOP condition (P) on the bus to end the transaction. The
receiver must acknowledge (A) or not-acknowledge (A) each byte received.
Figure 19-2 on page 204 shows a TWI transaction.
Figure 19-2. Basic TWI transaction diagram topology for a 7-bit address bus .
The master provides the clock signal for the transaction, but a device connected to the bus is allowed to stretch the low-
level period of the clock to decrease the clock speed.
TWI
DEVICE #1
RP
RS
SDA
SCL
VCC
TWI
DEVICE #2
RS
TWI
DEVICE #N
RS
Note: RS is optional
P
S
ADDRESS
6 ... 0
R/W
ACK
7 ... 0
DATA
ACK/NACK
7 ... 0
DATA
SDA
SCL
S
A
A/A
R/W
ADDRESS
DATA
P
A
DATA
Address Packet
Data Packet #0
Transaction
Data Packet #1
Direction
The slave provides data on the bus
The master provides data on the bus
The master or slave can provide data on the bus
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
PIC18F4321T-I/ML
IC PIC MCU FLASH 4KX16 44QFN
PIC18F4221T-I/ML
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX16 44QFN
PIC18F2321T-I/ML
IC PIC MCU FLASH 4KX16 28QFN
PIC18F2221T-I/SO
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX16 28SOIC
PIC16LF1939-I/MV
IC MCU 8BIT 28KB FLASH 40-UQFN
PIC24F16KL402-I/SP
IC MCU 16BIT 16KB FLASH 28-SPDIP
PIC18F24J11-I/SS
IC PIC MCU FLASH 16K 2V 28-SSOP
PIC24F16KA101-I/SO
IC PIC MCU FLASH 16K 20-SOIC
相关代理商/技术参数
PIC18F4450T-I/PT
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 16KB FL 768 RAM 34 I/O FS-USB 2.0 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455-BL
制造商:POWERLITE SYSTEMS 功能描述:PIC18F445 W/ BOOTLOADER FOR FLASHLAB 制造商:POWERLITE SYSTEMS 功能描述:PIC18F445 W/ BOOTLOADER, FOR FLASHLAB 制造商:POWERLITE SYSTEMS 功能描述:PIC18F445 W/ BOOTLOADER, FOR FLASHLAB; Silicon Manufacturer:Powerlite Systems; Core Architecture:PIC; Kit Contents:Board; Features:Bootloader Programming, RS232 Connector for Boot-Loading and Serial Comms ;RoHS Compliant: Yes
PIC18F4455-I/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455-I/P
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455-I/PT
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455T-I/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455T-I/PT
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4458-I/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24KB Flash 2KB RAM RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT